Microsoft Rolling Out Security Defaults: What You Need to Know
July 7th, 2022 | 4 min. read
Each day, Microsoft's Identity Security team blocks tens of millions of attacks. Sadly, some still get through, causing major damage to businesses. What's worse is that a lot of those attacks were preventable with good security hygiene. That's why to prevent such cases from happening, Microsoft has decided to roll out Azure AD Security Defaults for everybody. But, what does that mean for you?
According to the tech giant, many organizations still don't have a proper security team. That means even if a business wants to practice good cyber hygiene, they don't even know where to start. Security Defaults aims to address that by helping users get started on their cybersecurity journey.
At ITS, we are dedicated to helping businesses get a better understanding of cybersecurity so they can improve their defenses. We've helped hundreds of clients protect their networks from all kinds of threats, and we believe Security Defaults is a step in the right direction.
In this article, we'll dive into what it is, why it's important, and what to expect when it rolls out.
What is Microsoft Security Defaults?
 Security Defaults is a list of preconfigured security settings for all Microsoft accounts and products. That includes enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA), blocking legacy authentication protocols, and more. The rollout will impose those settings subscription-wide automatically. Although, you will still be given a choice of whether you want to opt-in or disable the settings altogether.
Security Defaults is a list of preconfigured security settings for all Microsoft accounts and products. That includes enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA), blocking legacy authentication protocols, and more. The rollout will impose those settings subscription-wide automatically. Although, you will still be given a choice of whether you want to opt-in or disable the settings altogether.
The main settings will include the following:
Require All Users to Register for Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA is an electronic authentication method where you are only granted access to a website or application after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence to an authentication mechanism. One example is when you try to log in to your email and are asked to input a code that will be generated and sent to your mobile – that is, MFA. Requiring that for everyone on your team is one of the simplest and most effective ways to prevent an attack.
Block Legacy Authentication Protocols
Legacy authentication is a term that refers to authentication requests made by users who don't use modern authentication methods. For example, someone using older versions of Office or mail protocols like IMAP, SMTP, or POP3. Many compromised sign-in attempts leverage them because an attacker can bypass MFA by using an older protocol. Once Security Defaults are enabled, all requests made by an older protocol will be blocked.
Protect Privileged Activities Like Access to the Azure Portal
People who have access to Azure Resource Manager can alter tenant-wide configurations, such as service settings and subscription billing. That's why users who can access those services must have additional security measures. After enabling Security Defaults, any user who will access such services will need to verify their identity with more authentication processes. This policy will apply to users who are accessing Azure Resource Manager services, whether they're an administrator or a user.
Who is Security Defaults For?
Microsoft Security Defaults is ideal for companies that want to increase their security posture but don't know where to start. It's a good first step on their cybersecurity journey. On the other hand, businesses with more complex security requirements might be a better fit for Conditional Access. That's because Conditional Access lets you configure policies with more granularity, including user exclusions, which aren't available in Security Defaults.
Benefits of Security Defaults
In 2019, Microsoft released Security Defaults for all new users to ensure basic security hygiene was in place. In particular, that included MFA and other modern authentication requirements. A few years later, there have already been over 30 million organizations with Security Defaults enabled, and they experience 80% less compromise overall.
Simply put, Security Defaults work. The best part is that it's free regardless of your license. You have nothing to lose and better security to gain. In fact, according to Microsoft's report, just enforcing MFA alone can help stop 99.9% of organization account compromises. It's one of the most effective yet underutilized security measures you can take, and Security Defaults will help you tap into that.
What to Expect When Security Defaults Rolls Out
Microsoft will enable Security Defaults based on usage patterns starting with organizations that are a good fit for it. More specifically, it will be available to companies that aren't using Conditional Access, haven't enabled Security Defaults in the past, and aren't actively using legacy authentication.
Global admins will then receive the notification in their email. They will then have the option to opt into Security Defaults right away or snooze for as many as 14 days. During this time, they can also explicitly opt-out of security defaults. After the initial grace period, Security Defaults will enable automatically, and users will then be asked to register using the Microsoft Authenticator app, while global administrators are going to be asked for a phone number.
And that's it. Once you opt-in, you immediately have a massively improved security posture against Identity-related attacks.
On the other hand, if you are actively using legacy authentication, you might need to consider upgrading to modern authentication processes. It might seem like a lot of work at first, but cybersecurity is worth all the effort.
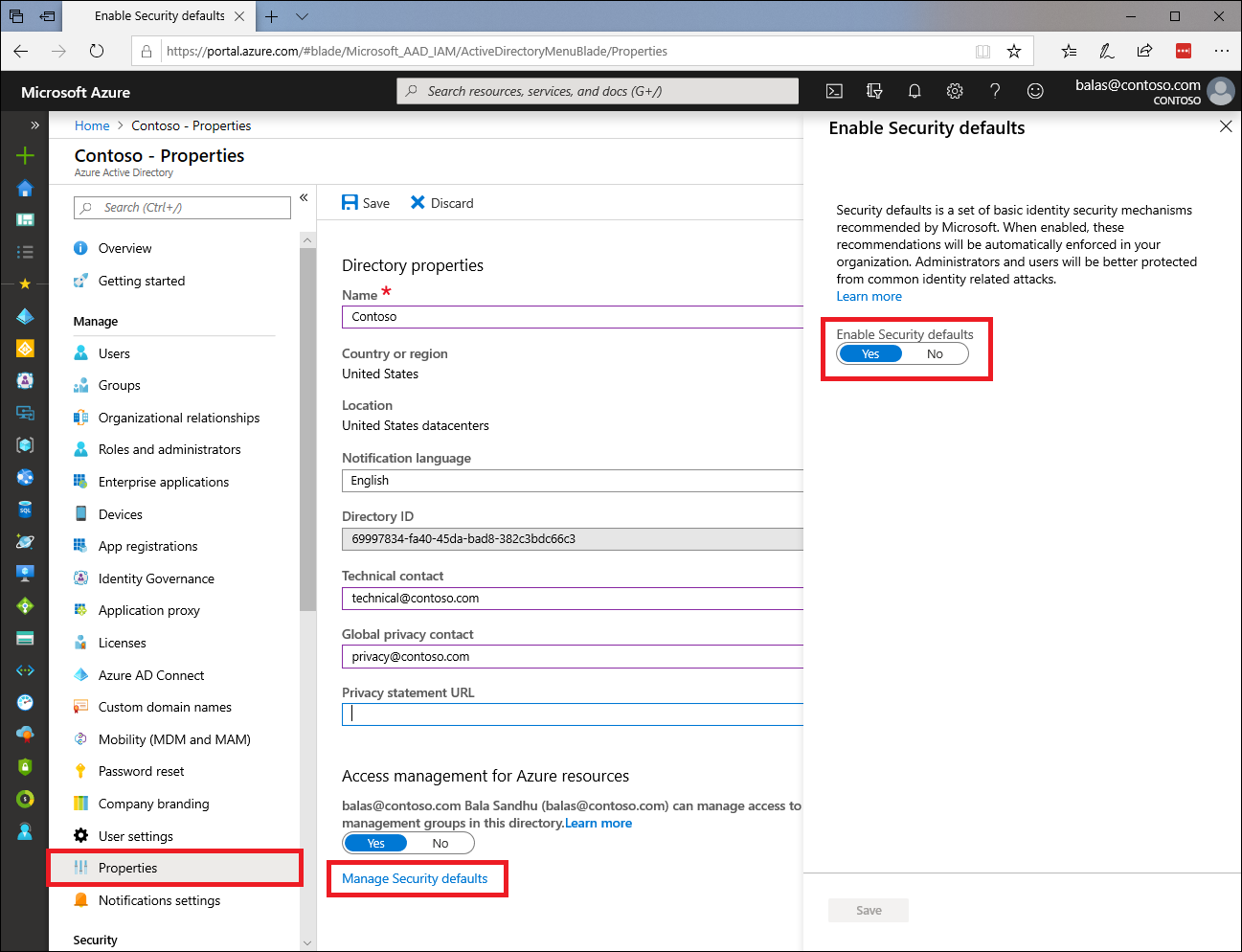
How to Enable Security Defaults
- Sign in to the Microsoft 365 admin center with security administrator, Conditional Access administrator, or Global admin credentials.
- Select Show All in the left pane, then under Admin centers, click on Azure Active Directory.
- Select Azure Active Directory in the left pane of the Azure Active Directory admin center.
- Select Properties in the Manage section on the dashboard's left menu.
- Select Manage Security defaults located at the bottom of the Properties page.
- You should see the Enable Security defaults setting in the right pane. If Yes is selected, then security defaults are already enabled, and no further action is required. If security defaults are not currently enabled, then select Yes to enable them, and then select Save.
Ready to Up Your Cybersecurity Baseline with Security Defaults?
Security Defaults is Microsoft's attempt at elevating the cybersecurity baseline of their users worldwide by collectively modernizing authentication mechanisms. It can help businesses looking to improve their security efforts but don't know where to start. In addition, it can effectively reduce the number of attacks your business could face. Overall, it's a good first step for companies that want to bolster their cyber defenses.
At ITS, we have helped hundreds of businesses improve their cybersecurity efforts and protect their networks from threats. From our experience, MFA is one of the easiest and most effective security measures you can deploy. If you want to get started ahead of the Security Defaults rollout, check out our article on how to set up MFA for Microsoft 365.
Mark Sheldon Villanueva has over a decade of experience creating engaging content for companies based in Asia, Australia and North America. He has produced all manner of creative content for small local businesses and large multinational corporations that span a wide variety of industries. Mark also used to work as a content team leader for an award-winning digital marketing agency based in Singapore.
Topics: